What is Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL)?
The Information Technology Infrastructure Library, commonly known as ITIL, is a comprehensive framework designed to standardize and improve IT service management (ITSM) practices across organizations. ITIL provides a set of best practices, guidelines, and processes that help businesses align their IT services with their overall business objectives, ensuring efficiency, reliability, and customer satisfaction. Initially developed in the 1980s by the UK government’s Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA),ITIL has evolved over the years and is now widely adopted by organizations worldwide, from small businesses to global enterprises.
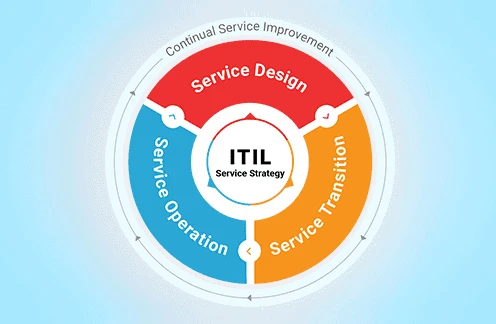
At its core, ITIL focuses on delivering value to customers by facilitating the effective management of IT services. It encompasses a lifecycle approach that covers the strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual improvement of IT services. This structured methodology allows organizations to manage their IT infrastructure more effectively, reduce downtime, improve service quality, and adapt to changing business needs. ITIL is not a rigid set of rules but rather a flexible framework that can be tailored to suit the unique requirements of any organization, regardless of industry or size.
One of the key aspects of ITIL is its emphasis on processes. Some of the most critical ITIL processes include incident management, problem management, change management, service desk operations, and service asset and configuration management. These processes help organizations handle issues efficiently, minimize disruptions, and maintain a high level of service availability. For example, incident management ensures that any disruptions to IT services are resolved quickly, while change management provides a structured approach to implementing updates or modifications without introducing new risks.
ITIL is currently in its fourth iteration, known as ITIL 4, which was released in 2019. This version builds on previous frameworks by incorporating modern practices such as Agile, DevOps, and Lean, while emphasizing the importance of value creation and collaboration. ITIL 4 introduces the Service Value System (SVS),which outlines how various components—such as processes, people, and technology—work together to deliver value to customers and stakeholders. It also includes the Four Dimensions of Service Management, which focus on organizations and people, information and technology, partners and suppliers, and value streams and processes.
For businesses, adopting ITIL offers numerous benefits. It enhances operational efficiency, reduces costs, improves customer satisfaction, and provides a clear framework for measuring and improving IT performance. ITIL certifications are also available for professionals, enabling them to gain expertise in ITSM and advance their careers. In essence, ITIL serves as a roadmap for organizations seeking to optimize their IT services, making it an indispensable tool in today’s technology-driven world.
How Does ITIL Work in IT Service Management?
The Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) is a cornerstone of IT service management (ITSM),providing a structured approach to delivering, managing, and improving IT services. ITIL works by offering a set of best practices and processes that organizations can implement to ensure their IT operations align with business goals, enhance service quality, and deliver value to customers. Rather than prescribing a one-size-fits-all solution, ITIL provides a flexible framework that can be adapted to meet the specific needs of any organization, making it a powerful tool for optimizing ITSM.
At the heart of ITIL’s functionality is its service lifecycle, which, in ITIL 4, is represented by the Service Value System (SVS). The SVS outlines how various components—such as governance, processes, and practices—interact to create value. The lifecycle begins with understanding demand and defining the value of a service, followed by designing, delivering, and continually improving that service. Key ITIL practices, such as service desk operations, incident management, problem management, and change management, are integrated into this lifecycle to ensure smooth operations. For instance, incident management focuses on restoring normal service operation as quickly as possible after a disruption, while change management ensures that updates or modifications are implemented without introducing risks.
ITIL works in ITSM by emphasizing a process-driven approach. Each process is designed to address specific aspects of service management, ensuring consistency and efficiency. For example, the service desk acts as a single point of contact for users, handling requests and resolving issues. Meanwhile, problem management digs deeper to identify and eliminate the root causes of recurring incidents, preventing future disruptions. By standardizing these processes, ITIL helps organizations reduce downtime, improve response times, and enhance overall service reliability.
In ITIL 4, the framework has evolved to incorporate modern methodologies like Agile, DevOps, and Lean, making it more adaptable to today’s fast-paced digital landscape. The Four Dimensions of Service Management—organizations and people, information and technology, partners and suppliers, and value streams and processes—ensure a holistic approach to ITSM. This means ITIL doesn’t just focus on technology but also considers the human element, collaboration with external partners, and the flow of value through the organization.
Ultimately, ITIL works in ITSM by providing a roadmap for organizations to manage their IT services proactively rather than reactively. It encourages continual improvement, enabling teams to assess performance, identify areas for enhancement, and implement changes effectively. By adopting ITIL, businesses can improve customer satisfaction, reduce operational costs, and achieve greater agility, making it an essential framework for modern IT service management.
Why ITIL Matters for Modern IT Operations
In today’s fast-paced, technology-driven world, the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) remains a critical framework for modern IT operations. As organizations increasingly rely on IT to drive business success, the need for efficient, reliable, and scalable IT service management (ITSM) has never been greater. ITIL matters because it provides a proven set of best practices that help organizations optimize their IT operations, align services with business goals, and deliver consistent value to customers. Its adaptability and focus on continual improvement make it an indispensable tool for navigating the complexities of modern IT environments.
One of the primary reasons ITIL matters is its ability to enhance operational efficiency. By standardizing processes such as incident management, change management, and service desk operations, ITIL reduces downtime, minimizes disruptions, and ensures faster resolution of issues. For example, in a modern IT operation where cloud computing, remote workforces, and digital transformation are the norm, ITIL’s structured approach helps teams manage complex infrastructures and maintain service availability. This efficiency translates to cost savings, improved resource utilization, and a better experience for both employees and customers.
ITIL also matters because it fosters alignment between IT and business objectives. In the past, IT departments were often seen as separate from core business functions, but today, IT is integral to driving innovation and growth. ITIL’s Service Value System (SVS) ensures that IT services are designed, delivered, and improved with the customer and business in mind. This alignment helps organizations respond to market changes, adopt new technologies, and meet customer expectations more effectively. For instance, ITIL’s focus on value creation ensures that IT operations support strategic goals, whether that’s launching a new product or improving customer service.
In the context of modern IT operations, ITIL’s integration with contemporary methodologies like Agile, DevOps, and Lean further underscores its relevance. ITIL 4, the latest iteration, embraces these practices, enabling organizations to remain agile and innovative while maintaining control over their IT services. This adaptability is crucial in an era where businesses must quickly pivot to new technologies, such as artificial intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT),or hybrid cloud environments.
Finally, ITIL matters because it promotes a culture of continual improvement. Modern IT operations are dynamic, with new challenges and opportunities emerging constantly. ITIL’s emphasis on assessing performance, identifying weaknesses, and implementing enhancements ensures that IT services evolve alongside business needs. By adopting ITIL, organizations can future-proof their operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and maintain a competitive edge in an increasingly digital landscape.
ITIL vs Other IT Frameworks: What Sets It Apart?
The Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) is one of many frameworks available for IT service management (ITSM) and IT operations, but its unique features and widespread adoption set it apart from alternatives like COBIT, ISO/IEC 20000, DevOps, and Lean IT. Understanding how ITIL compares to these frameworks can help organizations choose the right approach for their needs. While each framework has its strengths, ITIL’s comprehensive, process-driven methodology, flexibility, and focus on value creation make it a standout choice for modern IT management.
One key factor that sets ITIL apart is its holistic approach to ITSM. Unlike COBIT, which primarily focuses on IT governance and compliance, ITIL covers the entire service lifecycle—from strategy and design to operation and continual improvement. ITIL’s Service Value System (SVS) ensures that all aspects of IT services, including people, processes, and technology, work together to deliver value to customers. This end-to-end perspective makes ITIL particularly well-suited for organizations looking to optimize service delivery, not just ensure regulatory compliance.
Compared to ISO/IEC 20000, an international standard for ITSM, ITIL offers greater flexibility. While ISO/IEC 20000 provides a prescriptive set of requirements for certification, ITIL is a framework of best practices that organizations can adapt to their specific needs. This adaptability allows businesses of all sizes and industries to implement ITIL without being constrained by rigid mandates, making it more practical for diverse IT environments.
ITIL also distinguishes itself from DevOps, a methodology focused on collaboration between development and operations teams to accelerate software delivery. While DevOps emphasizes speed and agility, ITIL prioritizes structured processes and service quality. However, with the release of ITIL 4, the framework has integrated DevOps principles, allowing organizations to combine the agility of DevOps with ITIL’s focus on stability and value. This hybrid approach is a significant differentiator, enabling ITIL to remain relevant in fast-paced, agile-driven environments.
Lean IT, which focuses on eliminating waste and optimizing processes, shares some similarities with ITIL, particularly in its emphasis on efficiency. However, ITIL goes beyond Lean by providing a detailed set of practices for managing IT services, such as incident management, problem management, and change management. This depth and specificity give ITIL an edge for organizations seeking a comprehensive ITSM solution.
Ultimately, what sets ITIL apart is its balance of flexibility, depth, and adaptability. It can coexist with other frameworks, complementing their strengths while addressing their gaps. ITIL’s global recognition, extensive certification programs, and focus on continual improvement further solidify its position as a leading framework for ITSM, making it a versatile and powerful tool for modern IT operations.