What is IT Management?
IT management, or Information Technology management, refers to the process of overseeing and coordinating all aspects of an organization’s technology resources to ensure they align with its business objectives. It encompasses a wide range of activities, including the management of hardware, software, networks, data, and the people who maintain and operate these systems. At its core, IT management is about ensuring that technology serves as an enabler of business success rather than a hindrance, supporting operations, enhancing productivity, and driving innovation.
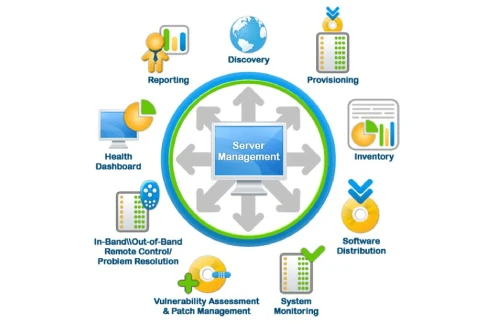
One of the primary responsibilities of IT management is to maintain and optimize an organization’s IT infrastructure. This includes managing servers, computers, storage systems, and networking equipment to ensure they function efficiently and reliably. IT managers must also oversee software applications, ensuring they meet the needs of employees and customers while remaining secure and up to date. This involves everything from selecting the right tools to implementing updates and patches to address vulnerabilities or improve performance.
Beyond infrastructure, IT management involves strategic planning and decision-making. IT managers work closely with other departments to understand their technology needs and develop solutions that support the organization’s goals. For example, they might implement a customer relationship management (CRM) system to improve sales processes or deploy cloud-based tools to enhance collaboration among remote teams. This strategic aspect of IT management requires a deep understanding of both technology and business, as well as the ability to anticipate future needs and trends.
Another critical component of IT management is cybersecurity. With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats, IT managers must prioritize the protection of sensitive data and systems. This involves implementing security measures such as firewalls, encryption, and multi-factor authentication, as well as developing policies to educate employees about safe technology use. IT management also includes disaster recovery planning to ensure that the organization can quickly recover from data breaches, hardware failures, or other disruptions.
IT management is not just about technology—it’s also about people. IT managers lead teams of professionals, including system administrators, developers, and support staff, ensuring they have the resources and training needed to perform their roles effectively. They also serve as a bridge between technical teams and non-technical stakeholders, translating complex concepts into actionable insights.
In summary, IT management is a multifaceted discipline that combines technical expertise, strategic planning, and leadership to harness the power of technology for organizational success. By overseeing infrastructure, aligning technology with business goals, ensuring security, and managing teams, IT management plays a vital role in helping businesses thrive in an increasingly digital world. Whether it’s improving operational efficiency, enhancing customer experiences, or driving innovation, IT management is the foundation that supports it all.
Key Components of IT Management
IT management is a complex and multifaceted discipline that relies on several key components to ensure the effective use of technology within an organization. These components work together to align IT operations with business goals, maintain system reliability, and drive innovation. Understanding these elements is essential for anyone looking to implement or improve IT management practices.
One of the foundational components of IT management is infrastructure management. This involves overseeing the physical and virtual components of an organization’s IT environment, including servers, computers, networking equipment, and storage systems. IT managers ensure that this infrastructure is reliable, scalable, and capable of supporting the organization’s current and future needs. This includes tasks such as monitoring system performance, upgrading hardware, and managing data centers or cloud-based resources to ensure seamless operations.
Another critical component is software management. This encompasses the selection, deployment, and maintenance of software applications that employees and customers rely on. IT managers must evaluate and choose tools that meet specific business needs, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, customer relationship management (CRM) software, or collaboration platforms. They also oversee software updates, troubleshoot issues, and ensure compatibility with existing systems, all while maintaining a focus on usability and efficiency.
Cybersecurity and risk management form another vital pillar of IT management. With cyber threats like malware, phishing, and ransomware on the rise, protecting an organization’s data and systems is a top priority. IT managers implement security measures such as firewalls, encryption, and access controls to safeguard sensitive information. They also develop and enforce security policies, conduct regular risk assessments, and establish disaster recovery plans to minimize the impact of potential breaches or system failures.
IT governance is another essential component, providing the framework for decision-making and accountability within the IT department. This includes defining policies, procedures, and standards to ensure that IT initiatives align with the organization’s strategic goals. IT governance also involves managing budgets, ensuring compliance with regulations, and measuring the return on investment (ROI) for technology initiatives. By establishing clear guidelines, IT governance helps organizations maximize the value of their IT resources.
Finally, people management is a key component that ties everything together. IT management is not just about technology—it’s about leading and supporting the teams that implement and maintain it. IT managers recruit, train, and oversee IT professionals, including system administrators, developers, and support staff. They foster a collaborative environment, provide ongoing education to keep skills current, and ensure that team members have the tools and resources needed to succeed.
IT Management Best Practices
IT management is a dynamic and critical function that requires a proactive and strategic approach to ensure technology supports organizational goals effectively. Implementing best practices in IT management can enhance efficiency, improve security, and drive innovation. Below are some of the most effective strategies to optimize IT management and deliver measurable results.
One of the cornerstone best practices is strategic alignment with business objectives. IT management should not operate in isolation; instead, it must align closely with the organization’s overall goals. This involves collaborating with business leaders to understand their needs and developing IT strategies that support key priorities, such as improving customer experience, increasing operational efficiency, or expanding market reach. Regularly reviewing and adjusting IT plans to reflect changing business needs ensures that technology remains a valuable asset rather than a liability.
Proactive maintenance and monitoring is another essential best practice. Rather than waiting for systems to fail, IT managers should implement routine monitoring and maintenance to identify and address potential issues before they escalate. This includes updating software, patching security vulnerabilities, and performing regular hardware checks. Using automated monitoring tools can provide real-time insights into system performance, allowing IT teams to respond quickly to anomalies and maintain uptime.
Prioritizing cybersecurity is non-negotiable in today’s threat landscape. Best practices in IT management include implementing a multi-layered security approach that combines firewalls, encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits. IT managers should also educate employees about cybersecurity risks, such as phishing attacks, and enforce policies like strong password requirements. Additionally, developing and testing a comprehensive disaster recovery plan ensures that the organization can quickly recover from cyberattacks, natural disasters, or system failures.
Adopting IT governance frameworks is a best practice that promotes accountability and efficiency. Frameworks like ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) or COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) provide structured guidelines for managing IT processes, from service delivery to risk management. These frameworks help standardize procedures, improve decision-making, and ensure compliance with industry regulations, ultimately enhancing the overall effectiveness of IT operations.
Investing in employee training and development is critical for successful IT management. Technology evolves rapidly, and IT teams must stay current with the latest tools, trends, and skills. Providing ongoing training opportunities—whether through workshops, certifications, or online courses—ensures that staff can effectively manage new systems and address emerging challenges. Additionally, fostering a culture of collaboration and communication within the IT team and across departments improves problem-solving and innovation.
Finally, leveraging data and analytics is a best practice that can transform IT management. By collecting and analyzing data on system performance, user behavior, and security incidents, IT managers can make informed decisions to optimize resources and improve processes. For example, analytics can reveal which applications are underutilized or identify patterns that indicate potential security threats, enabling proactive adjustments.
Choosing the Right IT Management Platform
Selecting the right IT management platform is a critical decision that can significantly impact an organization’s ability to manage its technology resources effectively. With a wide range of platforms available, each offering different features and capabilities, IT managers must carefully evaluate their options to find a solution that aligns with their specific needs and goals. Below are key considerations and steps to guide the process of choosing the right IT management platform.
The first step in selecting an IT management platform is defining organizational needs. Before exploring options, IT managers should assess their current IT environment and identify pain points, such as inefficient workflows, security vulnerabilities, or scalability challenges. Engaging stakeholders from different departments can provide valuable insights into the specific features required, such as asset management, network monitoring, or help desk support. A clear understanding of these needs will serve as a foundation for evaluating platforms and ensuring they address the organization’s unique requirements.
Scalability and flexibility are essential factors to consider when choosing an IT management platform. As businesses grow or adapt to changing conditions, their IT needs evolve. A platform that can scale to accommodate additional users, devices, or workloads without compromising performance is crucial. Additionally, the platform should be flexible enough to integrate with existing systems and support future technologies, such as cloud computing or artificial intelligence, to ensure long-term value.
Feature set and functionality play a pivotal role in the decision-making process. IT management platforms vary widely in their offerings, so it’s important to prioritize features that align with the organization’s goals. Common functionalities to look for include IT asset management (ITAM) to track hardware and software, network monitoring to ensure system performance, incident management for resolving issues, and reporting tools for data-driven insights. Some platforms also offer advanced capabilities like automated patch management, endpoint security, or remote monitoring and management (RMM),which can streamline operations and enhance security.
Ease of use and user experience are critical considerations, especially for teams with varying levels of technical expertise. A platform with an intuitive interface and clear navigation can reduce the learning curve and improve adoption rates among IT staff and end-users. IT managers should look for platforms that offer customizable dashboards, detailed documentation, and robust customer support to ensure smooth implementation and ongoing use.
Security and compliance are non-negotiable when selecting an IT management platform. The platform should include built-in security features, such as data encryption, role-based access controls, and audit logging, to protect sensitive information. Additionally, it should support compliance with industry standards and regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS, depending on the organization’s sector. Reviewing the platform’s security certifications and data privacy policies can provide assurance of its reliability.
Cost and return on investment (ROI) must also be evaluated. IT management platforms come with varying pricing models, such as subscription-based, per-user, or perpetual licensing fees. IT managers should consider not only the upfront cost but also the long-term value the platform provides, such as reduced downtime, improved efficiency, or enhanced security. Requesting demos, free trials, or case studies from vendors can help assess the platform’s ROI before making a commitment.